以下题目均来自leetcode、poj
实现栈-先进后出
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
push(x) – 元素 x 入栈 pop() – 移除栈顶元素 top() – 获取栈顶元素 empty() – 返回栈是否为空 注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作– 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
class MyStack {
private:
std::queue<int> _data;
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
std::queue<int> temp_queue;
temp_queue.push(x);
while(!_data.empty()){
temp_queue.push(_data.front());
_data.pop();
}
while(!temp_queue.empty()){
_data.push(temp_queue.front());
temp_queue.pop();
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int x = _data.front();
_data.pop();
return x;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return _data.front();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return _data.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = new MyStack();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
实现队列-先进先出
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
push(x) – 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。 pop() – 从队列首部移除元素。 peek() – 返回队列首部的元素。 empty() – 返回队列是否为空。 示例:
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.peek(); // 返回 1
queue.pop(); // 返回 1
queue.empty(); // 返回 false
说明:
你只能使用标准的栈操作 – 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。 假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用 pop 或者 peek 操作)。
class MyQueue {
private:
std::stack<int> _data;
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
std::stack<int> temp_stack;
while(!_data.empty()){
temp_stack.push(_data.top());
_data.pop();
}
temp_stack.push(x);
while(!temp_stack.empty()){
_data.push(temp_stack.top());
temp_stack.pop();
}
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int x = _data.top();
_data.pop();
return x;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
return _data.pop();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return _data.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
最小栈
设计一个支持 push,pop,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x) – 将元素 x 推入栈中。 pop() – 删除栈顶的元素。 top() – 获取栈顶元素。 getMin() – 检索栈中的最小元素。 示例:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack(); minStack.push(-2); minStack.push(0); minStack.push(-3); minStack.getMin(); –> 返回 -3. minStack.pop(); minStack.top(); –> 返回 0. minStack.getMin(); –> 返回 -2.
class MinStack {
public:
stack<int> data;
stack<int> minstack;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
data.push(x);
if(minstack.empty()){
minstack.push(x);
}else{
if(x>minstack.top()){
x = minstack.top();
}
minstack.push(x);
}
}
void pop() {
data.pop();
minstack.pop();
}
int top() {
return data.top();
}
int getMin() {
return minstack.top();
}
};
栈顺序
已知1到n的数字序列,按顺序入栈,每个数字入栈后,可以停留后马上出栈,也可停留后,等待后面数入栈出栈后,再出栈,求出栈数字序列是否合法。
32541合法,31245不合法
bool checkIsValidOrder(queue<int>& order){
stack<int> s;
int n = order.size();
for(int i = 1;i <=n; i++){
s.push(i);
while(!s.empty() && s.top() == order.front()){
s.pop();
order.pop();
}
}
if(!s.empty()){
return false;
}
return true;
}
计算器
实现一个基本的计算器来计算一个简单的字符串表达式的值。
字符串表达式可以包含左括号 ( ,右括号 ),加号 + ,减号 -,非负整数和空格 。
示例 1:
输入: “1 + 1” 输出: 2 示例 2:
输入: “ 2-1 + 2 “ 输出: 3 示例 3:
输入: “(1+(4+5+2)-3)+(6+8)” 输出: 23 说明:
你可以假设所给定的表达式都是有效的。 请不要使用内置的库函数 eval。
class Solution {
public:
void compute(stack<int> &number_stack,stack<char>& operation_stack){
if(number_stack.size() < 2){
return;
}
int num2 = number_stack.top();
number_stack.pop();
int num1 = number_stack.top();
number_stack.pop();
if(operation_stack.top() == '+'){
number_stack.push(num1+num2);
}else if(operation_stack.top() == '-'){
number_stack.push(num1-num2);
}
operation_stack.pop();
}
int calculate(string s) {
static const int STATE_BEGIN = 0;
static const int NUMBER_STATE = 1;
static const int OPERATION_STATE = 2;
stack<int> number_statck;
stack<char> operation_stack;
int number = 0;
int state = STATE_BEGIN;
int compute_flag = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < s.length();i++){
if(s[i] == ' '){
continue;
}
switch(state){
case STATE_BEGIN:
if(s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'){
state = NUMBER_STATE;
}else{
state = OPERATION_STATE;
}
i--;
break;
case NUMBER_STATE:
if(s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'){
number = number*10+s[i]-'0';
}else{
number_stack.push(number);
if(compute_flag == 1){
compute(number_stack,operation_stack);
}
number = 0;
i--;
state = OPERATION_STATE;
}
break;
case OPERATION_STATE:
if(s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-'){
operation_stack.push(s[i]);
compute_flag = 1;
}else if(s[i] == '('){
state = NUMBER_STATE;
compute_flag = 0;
}else if(s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'){
state = NUMBER_STATE;
i--;
}else if(s[i] == ')'){
compute(number_stack,operation_stack);
}
break;
}
}
if(number != 0){
number_stack.push(number);
compute(number_stack,operation_stack);
}
if(number == 0 && number_stack.empty()){
return 0;
}
return number_stack.top();
}
};
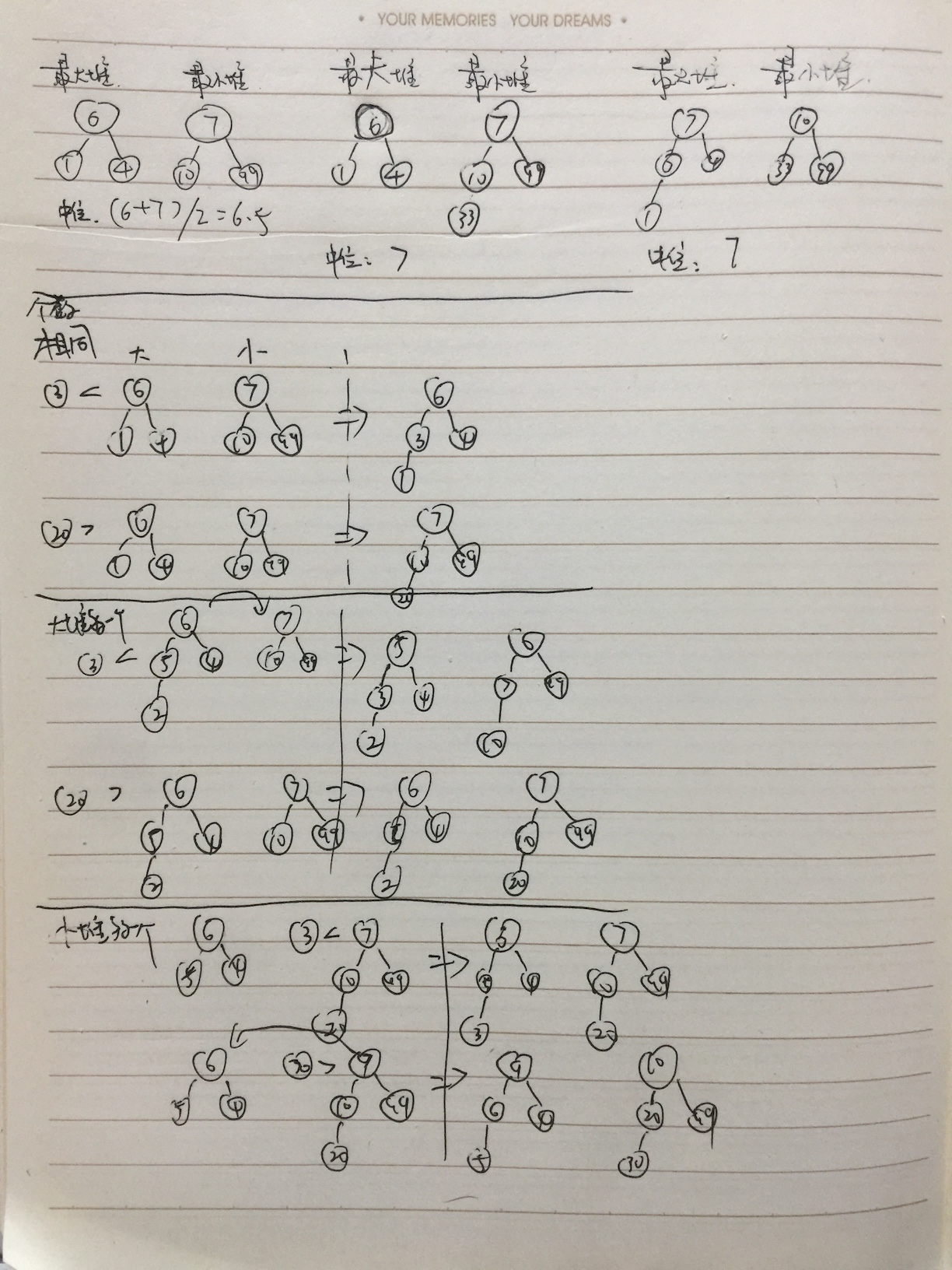
最大和最小二叉堆
当父节点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最大堆。 当父节点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最小堆
数组中的第K个最大元素
在未排序的数组中找到第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2 输出: 5 示例 2:
输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] 和 k = 4 输出: 4 说明:
你可以假设 k 总是有效的,且 1 ≤ k ≤ 数组的长度。
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
std::priority queue<int,std::vector<int>,std::greater<int>> q;
for(int = 0;i < nums.size();i++){
if(q.size() < k){
q.push(nums[i]);
}else if(q.top() < nums[i]){
q.pop();
q.push(nums[i]);
}
}
return q.top();
}
};
数据流的中位数
中位数是有序列表中间的数。如果列表长度是偶数,中位数则是中间两个数的平均值。
例如,
[2,3,4] 的中位数是 3
[2,3] 的中位数是 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5
设计一个支持以下两种操作的数据结构:
void addNum(int num) - 从数据流中添加一个整数到数据结构中。 double findMedian() - 返回目前所有元素的中位数。 示例:
addNum(1) addNum(2) findMedian() -> 1.5 addNum(3) findMedian() -> 2 进阶:
如果数据流中所有整数都在 0 到 100 范围内,你将如何优化你的算法? 如果数据流中 99% 的整数都在 0 到 100 范围内,你将如何优化你的算法?
class MedianFinder {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MedianFinder() {
}
//动态维护一个最大堆和一个最小堆,分别存储一半的数据,维持最大堆的堆顶比最小堆得堆顶小。
void addNum(int num) {
if(big_queue.empty()){
big_queue.push(num);
return;
}
if(big_queue.size() == small_queue.size()){
if(num < big_queue.top()){
big_queue.push(num);
}else{
small_queue.push(num);
}
}else if(big_queue.size() > small_queue.size()){
if(num > big_queue.top()){
small_queue.push(num);
}else{
small_queue.push(big_queue.top());
big_queue.pop();
big_queue.push(num);
}
}else if(big_queue.size() < small_queue.size()){
if(num < small_queue.top()){
big_queue.push(num);
}else{
big_queue.push(small_queue.top());
small_queue.pop();
small_queue.push(num);
}
}
}
double findMedian() {
if(big_queue.size() == small_queue.size()){
return (big_queue.top() + small_queue.top())/2;
}else if(big_queue.size() > small_queue.size()){
return big_queue.top();
}
return small_queue.top();
}
};
/**
* Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MedianFinder* obj = new MedianFinder();
* obj->addNum(num);
* double param_2 = obj->findMedian();
*/