以下题目均来自leetcode、poj
树的定义
树是一种数据结构,它是由n(n>=1)个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。
树具有的特点有:
(1)每个结点有零个或多个子结点
(2)没有父节点的结点称为根节点
(3)每一个非根结点有且只有一个父节点
(4)除了根结点外,每个子结点可以分为多个不相交的子树。
二叉树的定义
二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构。它有五种基本形态:二叉树可以是空集;根可以有空的左子树或右子树;或者左、右子树皆为空。
性质1:二叉树第i层上的结点数目最多为2的i-1次方(i>=1)
性质2:深度为k的二叉树至多有2的k次方-1个结点(k>=1)
性质3:包含n个结点的二叉树的高度至少为:$ log2^{n}+1 $
性质4:在任意一棵二叉树中,若终端结点的个数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则n0=n2+1
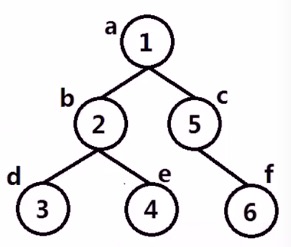
深度遍历
前序遍历:先范文父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树。
中序遍历:首先遍历左子树,然后再访问父节点,最后遍历右子树。
后序遍历:首先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问父节点。
struct TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x):val(x),left(NULL),right(NULL){}
};
void traversal(TreeNode *node){
if(!node){
return;
}
//此时访问node称为前序遍历,(完成一次递归前)
traversal(node->left);
//此时访问node称为中序遍历 (完成一次递归后)
traversal(node->right);
//此时访问node称为后序遍历 (完成二次递归后)
}
//前 a1,b2,d3,e4,c5,f6
//中 d3,b2,e4,a1,c5,f6
//后 d3,e4,b2,f6,c5,a1
路径总和 II
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
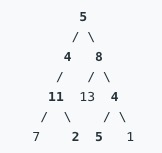
返回:
[ [5,4,11,2], [5,8,4,5] ]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
path_value = 0;
preOrder(root,path_value,sum,path,result);
return result;
}
private:
void preOrder(TreeNode *node,
int &path_value,
int sum,
vector<int> &path,
vector<vector<int>>& result){
if(!node){
return;
}
//前序放入栈
path_value +=node->val;
path.push_back(node->val);
//是叶节点(没有左右子节点)
if(sum == path_value&&
!node->left&&
!node->right){
reuslt.push_back(path);
}
preOrder(node->left,path_value,sum,path,result);
preOrder(node->right,path_value,sum,path,result);
//遍历完,扔掉
path_value -=node->val;
path.pop_back();
}
};
最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
示例 1:
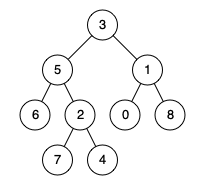
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出: 3
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
vector<TreeNode*> path;
vector<TreeNode*> nodePPath;
vector<TreeNode*> nodeQPath;
int finish = 0;
preOrder(root,p,path,nodePPath,finish);
path.clear();
finish = 0;
preOrder(root,q,path,nodeQPath,finish);
int path_len = 0;
pathLen = nodePPath.size() < nodeQPath.size() ? nodePPath.size() : nodeQPath.size();
TreeNode* result = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < path_len;i++){
if(nodePPath[i] == nodeQPath[i]){
result = nodePPath[i];
}
}
return result;
}
private:
void preOrder(TreeNode* node,
TreeNode* search,
vector<TreeNode*>& path,
vector<TreeNode*>& result,
int &finish
){
if(!node || finish){
return;
}
path.push_back(node);
if(node == search){
finish = 1;
result = path;
}
preOrder(node->left,search,path,result,finish);
preOrder(node->right,search,path,result,finish);
path.pop_back();
}
};
二叉树展开为链表
给定一个二叉树,原地将它展开为链表。
例如,给定二叉树

将其展开为:
1-2-3-4-5-6
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//借助
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
std::vector<TreeNode*> nodeVec;
preOrde(root,nodeVec);
for(int i = 1;i < nodeVec.size();i++){
nodeVec[i-1].left = NULL;
nodeVec[i-1].right = nodeVec[i];
}
}
private:
void preOrder(TreeNode* node,std::vector<TreeNode*> &nodeVec){
if(!node){
return;
}
nodeVec.push_back(node);
preOrder(node->left,nodeVec);
preOrder(node->right,nodeVec);
}
};
//就地
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode *last = NULL;
preOrder(root,last);
}
private:
void preOrder(TreeNode* node,TreeNode &last){
if(!node){
return;
}
if(!node->left && !node->right){
last = node;
return;
}
TreeNode *left = node->left;
TreeNode *right = node->right;
TreeNode *left_last = NULL;
TreeNode *right_last = NULL;
if(left){
//先处理左子树为链表
preOrder(left,left_last);
node->left = NULL;
node->right = left;
last = left_last;//左子树最后一个
}
if(right){
preOrder(right,right_last);
if(leftLast){
//左子树最后一个节点接上右子树
left_last->right = right;
}
last = right_last;
}
}
};
宽度遍历

层次遍历: a1,b2,c5,d3,e4,f6
void BFS_print(TreeNode* root){
std::queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push_back(root);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%d",node->val);
if(node->left){
q.push(node->left);
}
if(node->right){
q.push(node->right);
}
}
}
二叉树的右视图
给定一棵二叉树,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4] 输出: [1, 3, 4] 解释:

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//层次遍历二叉树,每层中的最后一个节点。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
std::vector<int> view;
std::queue<std::pair<TreeNode*,int>> q;
if(root){
q.push(std::make_pair(root,0));
}
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* node = q.front().first;
int depth = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if(view.size() == depth){
//第一次放入
view.push_back(node->val);
}else{
//存在则更新
view[depth] = node->val;
}
if(node->left){
q.push(std::make_pair(node->left,depth+1));
}
if(node->right){
q.push(std::make_pair(node->right,depth+1));
}
}
}
};
图
无向图和有向图、带权图和不带权图
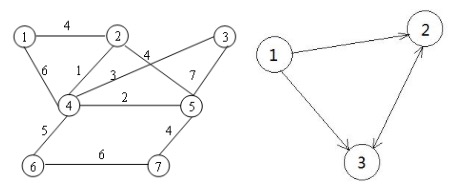
一般用邻接矩阵、邻接表来表示。
深度搜索
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode*> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x):label(x){};
};
void DFS_graph(GraphNode* node,int visit[]){
visit[node->label] = 1;
printf("%d",node->label);
for(int i = 0;i < node->neighbors.size();i++){
if(visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
DFS_graph(node->neighbors[i],visit);
}
}
}
宽度搜索
void DFS_graph(GraphNode* node,int visit[]){
std::queue<GraphNode*> q;
q.push(node);
visit[node->label] = 1;
while(!q.empty()){
GraphNode *node = q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%d",node->label);
for(int i = 0;i < node->neighbors.size();i++){
if(visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
q.push(node->neighbors[i]);
visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] = 1;
}
}
}
}
课程表
现在你总共有 n 门课需要选,记为 0 到 n-1。
在选修某些课程之前需要一些先修课程。 例如,想要学习课程 0 ,你需要先完成课程 1 ,我们用一个匹配来表示他们: [0,1]
给定课程总量以及它们的先决条件,判断是否可能完成所有课程的学习?
示例 1:
输入: 2, [[1,0]] 输出: true 解释: 总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要完成课程 0。所以这是可能的。 示例 2:
输入: 2, [[1,0],[0,1]] 输出: false 解释: 总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要先完成课程 0;并且学习课程 0 之前,你还应先完成课程 1。这是不可能的。 说明:
输入的先决条件是由边缘列表表示的图形,而不是邻接矩阵。详情请参见图的表示法。 你可以假定输入的先决条件中没有重复的边。 提示:
这个问题相当于查找一个循环是否存在于有向图中。如果存在循环,则不存在拓扑排序,因此不可能选取所有课程进行学习。 通过 DFS 进行拓扑排序 - 一个关于Coursera的精彩视频教程(21分钟),介绍拓扑排序的基本概念。 拓扑排序也可以通过 BFS 完成。
//判断有向图是否有环
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode*> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x):label(x){};
};
//深度
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
std::vector<GraphNode*> graph;
std::vector<int> visit;
for(int i = 0;i < numCourses;i++){
graph.push_back(new GraphNode(i));
visit.push_back(-1);
}
for(int i = 0;i < prerequisites.size();i++){
GraphNode *begin = graph[prerequisites[i].second];
GraphNode *end = graph[prerequisites[i].first];
begin->neighbors.push_back(end);//课程2指向课程1
}
for(int i = 0;i < graph.size();i++){
//是否有环
if(visit[i] == -1 && !DFS_graph(graph[i],visit)){
return false;
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < numCourses;i++){
delete graph[i];
}
return true;
}
private:
bool DFS_graph(GraphNode* node,std::vector<int> &visit){
//-1没有访问过,0正在访问,1代表已完成访问
visit[node->label] = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < node->neighbors.size();i++){
if(visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == -1){
//有环
if(DFS_graph(node->neighbors[i],visit) == 0){
return false;
}
}
else if(visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
//指向自己
return false;
}
}
visit[node->label] = 1;
return true;
}
};
//宽度
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {
std::vector<GraphNode*> graph;
std::vector<int> degree;
for(int i = 0;i < numCourses;i++){
degree.push_back(0);
graph.push_back(new GraphNode(i));
}
for(int i = 0;i < prerequisites.size();i++){
GraphNode *begin = graph[prerequisites[i].second];
GraphNode *end = graph[prerequisites[i].first];
begin->neighbors.push_back(end);//<课程1,课程2>
degree[prerequisites[i].first]++;//课程1入度
}
std::queue<GraphNode*> q;
for(int i = 0;i < numCourses;i++){
if(degree[i] == 0){
q.push(graph[i]);
}
}
while(!q.empty()){
//完成一次搜索从队列中取出
GraphNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0;i < node->neighbors.size();i++){
//指向的所有节点入度减1
degree[node->neighbors[i].label]--;
//入度为0的添加到队列
if(degree[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
q.push(node->neighbors[i]);
}
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < numCourses;i++){
delete graph[i];
}
//所有入度为0,则图无环
for(int i = 0;i < degree.size();i++){
if(degree[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};