早先在CSDN发表的《C#数据结构》文章重新整理一下
System.Array
Array提供一些方法,用于创建、处理、搜索数组并对数组进行排序,从而充当公共语言运行时中所有数组的基类。
Array具有固定的容量,必须在声明时指定长度。 若要增加容量,你必须创建一个新Array对象所需的容量、 复制元素从旧Array到新对象,并删除旧Array。
数组存储在连续的内存上,数组可以直接通过下标访问,索引查找速度快,存储类型一致。
using System;
namespace TestCSharp
{
#region MainCalss
class MainClass
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
//初始
int[] charList = new int[100];
//charList[100] = 200;Error
string[] nameList = { "Bob", "Conie", "Jennifer" };
int[,] mapList = new int[3, 4];//mapList.Length = 12;
int[,] maskList = { { 1, 0, 1 }, { 4, 0, 5 }, { 6, 0, 7 }, { 16, 0, 17 } };
string[][] itemList = new string[5][];
itemList[4] = new string[3] { "a", "b", "c" };
itemList[2] = new string[4] { "a", "b", "c", "d" };
//遍历
foreach (string t in nameList)
{
Console.WriteLine(t);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nameList.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(nameList[i]);
}
foreach (var s in maskList)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
for (int i = 0; i < itemList.Length; i++)
{
if (itemList[i] != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("i:{0},length:{1}",i,itemList[i].Length);
}
}
}
}
#endregion
}
在for遍历时,不推荐上面的写法,可修改为如下
int total = nameList.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(nameList[i]);
}
System.Collections.ArrayList
ArrayList可以理解为可以动态增加内存的数组
-
不必在声明时指定长度,会根据存储的数据动态增加或减少长度
-
可以灵活的插入或删除元素,在插入和删除元素时会进行拆箱和装箱的操作,消耗性能,效率低;且会移动它之后所有元素的位置,效率也低。
-
可以灵活访问元素
-
存储类型可以不一致,因为把不同的类型都当做Object来做处理,有拆箱和封箱的效率损耗。
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace TestCSharp
{
class MainClass
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
ArrayList nameList = new ArrayList();
nameList.Add("Bob");
nameList.Remove("Bob");
Console.WriteLine(nameList.Count);
Console.WriteLine(nameList.Contains("Bob"));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
nameList.Add("Unkowned");
}
nameList.Insert(1,"Conie");
nameList.Capacity = 50;
ArrayList otherList = new ArrayList(new string[]{"Jennifer","Ben"});
nameList.InsertRange(3,otherList);
Console.WriteLine(nameList.IndexOf("Ben"));//4
nameList.RemoveAt(1);
nameList.Reverse();
foreach (var name in nameList)
{
Console.WriteLine(name);
}
Console.WriteLine("");
nameList.Sort();
for (int i = 0; i < nameList.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(nameList[i]);
}
nameList.Add(123);
nameList.Clear();
}
}
}
System.Collections.Generic.List
List < T > 是一种范型,需要在声明时通过泛型指定类型,解决了ArrayList对于值类型需要装箱拆箱的缺点。需要处理的元素数量不确定时,通常建议使用。
System.Collections.Generic.LinkedList
LinkedList < T > 链表适合元素数量不固定,需要经常增减节点的情况,链表在内存中的空间不是连续的,每块空间称作一个节点,每个节点都存有与它之前和之后相连接的节点的地址,因此向链表中添加和删除元素时只需要更改相关节点存储的地址的指向,插入和删除是 o(1)的操作,效率高。查找元素时不能通过下标访问,只能从头开始通过地址按顺序查找,效率低
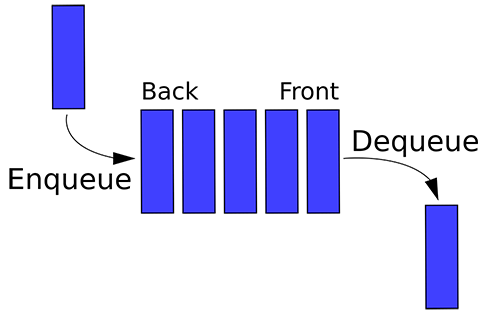
Queue
Queue 表示对象的先进先出集合
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace TestCSharp
{
#region MainCalss
class MainClass
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Queue q = new Queue();
q.Enqueue("Bob");
q.Enqueue("Conie");
q.Enqueue("Jennifer");
Console.WriteLine(q.Dequeue());//Bob
}
}
#endregion
}
Stack
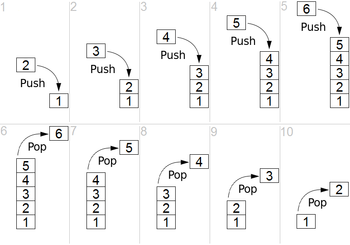
Stack 表示可变大小的后进先出 (LIFO) 集合
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace TestCSharp
{
#region MainCalss
class MainClass
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stack s = new Stack();
s.Push("1");
s.Push("2");
s.Push("3");
s.Push("4");
s.Push("5");
s.Push("6");
Console.WriteLine(s.Pop());//6
}
}
#endregion
}
System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary
Dictionary<TKey,TValue>表示键和值的集合。可以通过key快速查找对应的value,速度快,,但是消耗内存。相比list,它的添加会慢。
Dictionary<string, string> openWith = new Dictionary<string, string>();
openWith.Add("bob", "bob.exe");
openWith.Add("connie", "connie.exe");
openWith.Add("Jennifer", "Jennifer.exe");
openWith["tony"] = "tony.exe";
openWith.Remove("tony");
foreach( KeyValuePair<string, string> kvp in openWith )
{
Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}",
kvp.Key, kvp.Value);
}
Hashtable
Hashtable表示根据键的哈希代码进行组织的键/值对的集合。Dictionary支持泛型,而Hashtable不支持
HashSet
HashSet
参考资料:
Dictionary part 1, hash tables
Dictionary part 2, .NET implementation